One of the most painful and unfortunately common types of infections is an ingrown toenail infection. Roughly 2 out of 10 people who seek a doctor for their foot problem have an ingrown toenail as the source of the problem. To treat and prevent future ingrown toenails and ingrown toenail infections from occurring, you may desire to know more about the causes, signs, and treatments of this condition. In this article, we’ll discuss what causes infected ingrown toenails, what some signs of infection are (including after surgery for this condition), and the different treatment options available to bring you effective relief.
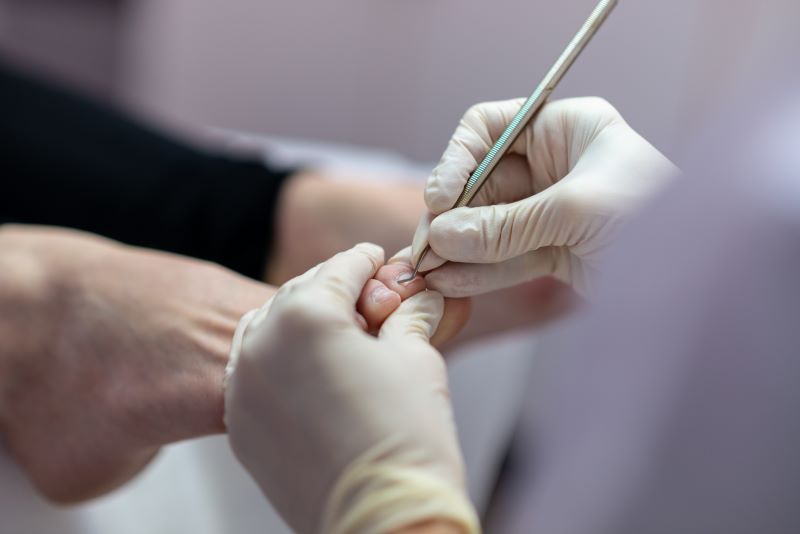 What Causes an Infected Ingrown Toenail?
What Causes an Infected Ingrown Toenail?
An ingrown toenail occurs when the corner tip or edge of a toenail pierces the toenail skin and subsequently grows back into it. It is a painful condition that can happen to any person and also occurs primarily in the big toes. If left untreated, ingrown toenails can also cause some infections that can spread into some of the underlying bone structures of the given foot. Other conditions you may have that reduce the blood flow to the feet, such as peripheral arterial disease or diabetes, can make ingrown toenails more likely to occur. People that have these types of conditions can also have some severe complications if a toenail infection occurs.
Some other relatively common causes of ingrown toenails before infection potentially occurs include not trimming your toenails straight across, cutting toenails too short, wearing uncomfortable or otherwise small shoes that crowd the toenails, a toenail injury, a nail infection, or having very curved toenails. Other factors that can potentially increase your risk of having an ingrown toenail are being at a young age, when feet often perspire more (leading to softening of the skin and toenails), or participating in activities that pose an increased risk of toe injuries, such as running and kicking activities.
Symptoms of an Ingrown Toenail Infection
Analogous to many other potentially serious conditions, an ingrown toenail may begin with some relatively minor symptoms. However, these initially minor symptoms can escalate and become more and more serious and afflicting as time goes on. Due to this potential to escalate without proper attention and treatment, it’s important to pay close attention to any early symptoms of an ingrown toenail to prevent a subsequent infection or a complication.
Some of the early symptoms of an infected ingrown toenail can include swelling, hardening, or redness of the skin around the nail, some pressure under the nail, pain when touched, throbbing, or oozing or build-up of fluid. Other early symptoms include bleeding, a foul smell, a pus-filled abscess in the area where the nail punctured the toe skin, warmth in the area that is around the nail, overgrowth of inflamed, new tissue around the edges of the nail, and cracked, thick, and yellowing nails. This last symptom occurs specifically in fungal infections.
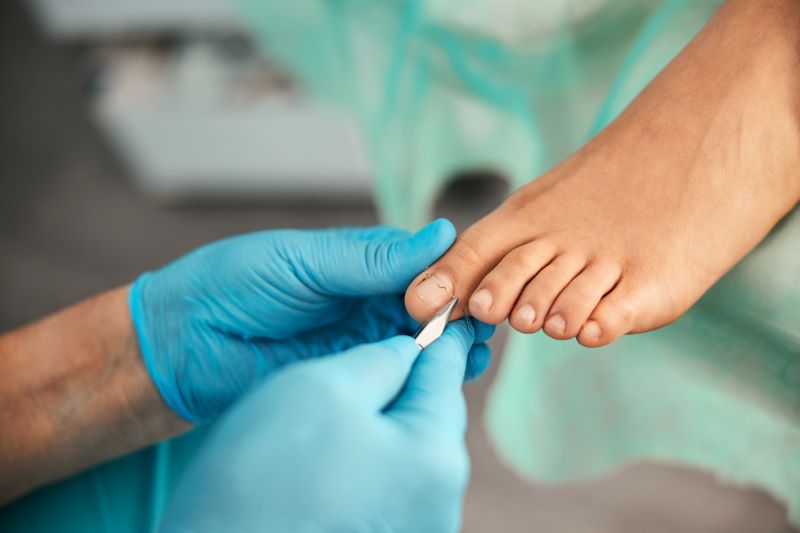 Ingrown Toenail Infection Risks
Ingrown Toenail Infection Risks
You should see your health care provider if you have diabetes or a different condition that gives rise to poor blood flow in your feet and you have a foot infection or sore. With an ingrown toenail, you can have either a bacterial or fungal infection. MRSA, for example, is a drug-resistant staph infection that lives on the skin. Ingrown toenails can cause this type of potentially deadly infection. Any current conditions that cause nerve damage to your feet or reduce blood flow can hinder healing, making infections not only more likely but also harder to treat. These infections can cause other complications such as gangrene which can require surgery.
Ingrown Toenail Infection Treatments
There are a couple of main treatment options available for an ingrown toenail infection, and the process with your podiatrist can include techniques with chemical intervention or without. The goal is to remove the section of the nail that is causing discomfort and protruding. Without the use of chemicals, hopes are that the toenail will effectively regrow to its original, natural proportions. If the toenail does regrow back into the same problem area, the podiatrist will then use chemical phenol to prevent growth in the area of chemical phenol application. Unless a podiatrist properly addresses the toenail infection, it can set in and worsen in a short time.
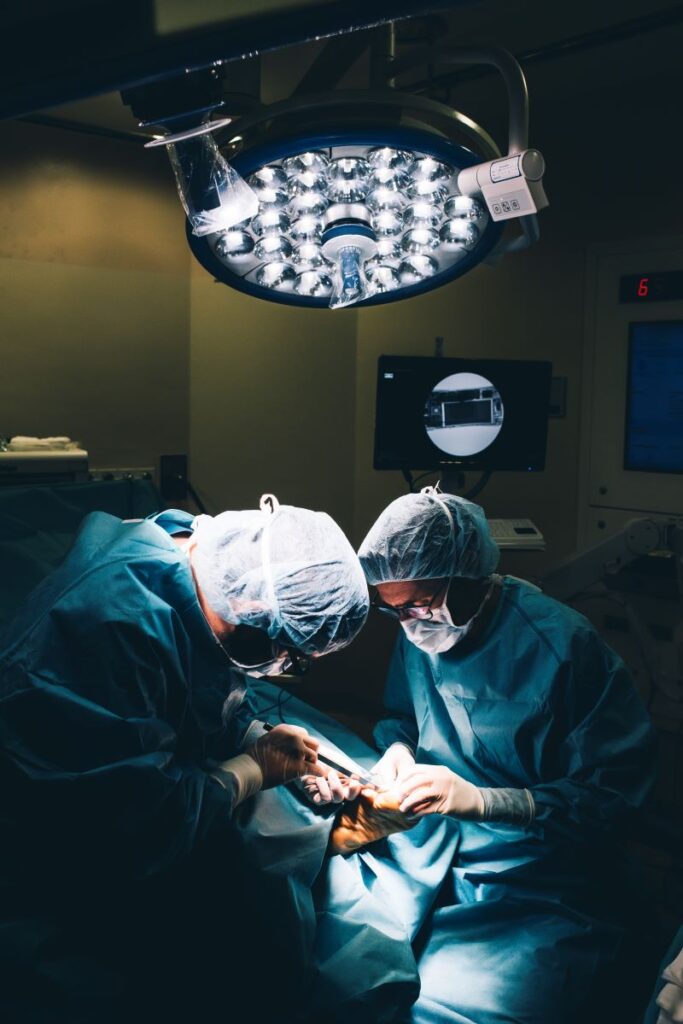 Ingrown Toenail Surgery
Ingrown Toenail Surgery
Sometimes, an ingrown toenail or ingrown toenail infection cannot experience proper healing without the need for invasive surgery. You may need to consider surgery with your podiatrist in the event of a more serious or recurring ingrown toenail or infection. If a bone infection occurs, the doctor may give you a blood test to see how deep the toenail infection is. Other tests they may perform can include an MRI, X-ray, bone scan, or bone biopsy in rare cases. A major way to prevent a more severe ingrown toenail, infection, or the need for toenail surgery is to regularly observe signs, contributing factors, and to consult a doctor before these aspects worsen at all.
If you need and effectively undergo surgery, it’s also important to monitor and take note of any subsequent signs of infection after ingrown toenail surgery. Following surgery, it’s important to take care of your feet to aid recovery and prevent future infection. You can speed up recovery by soaking the foot in Epson salt daily, taking an anti-inflammatory drug, applying antibiotic ointment, and keeping the wound dry and clean. It should heal within several weeks. Minor complications of surgery are common. However, an infection may develop after surgery due to the open wound. Consult your doctor for signs to prevent serious damage and to aid recovery.
Experience Speedy Relief of Ingrown Toenail Infections
If you have a toenail you worry may be ingrown, is starting to cause you discomfort, or you fear might worsen into an infected ingrown toenail, see the Foot & Ankle Specialists of Illinois for careful, attentive treatment. Ingrown toenails can worsen severely as time passes. Save yourself increased pain, complications, and medical costs by seeking treatment today.

