Are Warts Contagious?
Warts are benign growths that develop on the skin of different body parts. They can come in various forms, and their cause is viruses. Highly common, the majority of people will develop at least one wart at some point in their lives. Warts can affect people of all ages but are most common in teenagers and children. The majority of warts are harmless but can be bothersome. As such, many wonder how contagious they are. In this article, we’ll discuss what verruca Vulgaris is, the symptoms of verruca Vulgaris, and what causes viral warts. We’ll also discuss how contagious warts are and the different treatment options for warts.
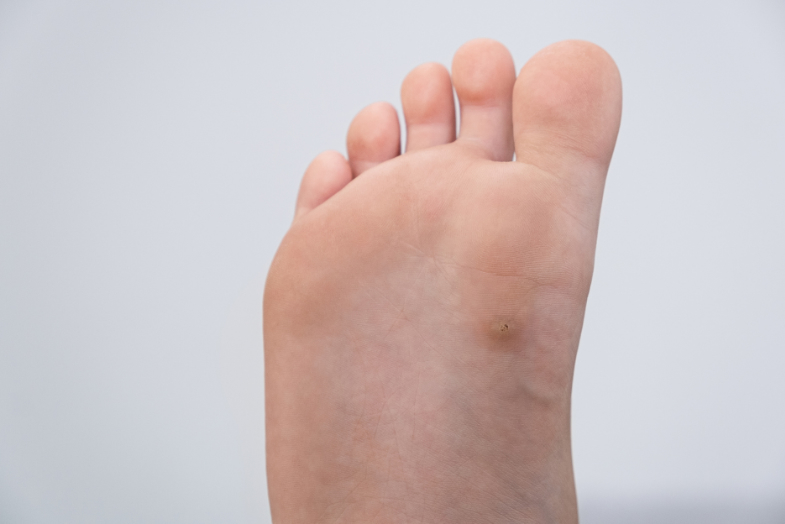 What Is Verruca Vulgaris?
What Is Verruca Vulgaris?
Verruca Vulgaris, also known as the common wart, is a benign skin growth often caused by a local infection of one of the human papillomavirus types. These DNA viruses are of the Papovavirus group. Especially common in children and adolescents, warts can develop on any mucocutaneous surface. A large percentage of warts occur on the hands. Typical viral warts present as a rough-surfaced nodule of a light or dark color compared to the surrounding skin. Viral warts are different from “senile warts” or seborrheic keratosis. That type of wart usually appears in older persons and isn’t contagious or harmful but is permanent.
While generally less harmful, warts can affect social activities. Lesions may become uncomfortable or bleed. The HP types that cause warts are 1, 2, 4, 27, 57, and 63. These warts occur most often in people ages 5-to-20 years old. Only around 15% of warts occur in people aged 35 or older. HPV-2 is the most common type causing warts in butchers. HPV-7 causes up to 27% of hand warts in these high-risk individuals. HPV-7 is rarely the cause of warts in the general population. The history of warts dates back as far as 400 BC when the Greek physician Hippocrates gave one of the first descriptions of warts.
Symptoms of Verruca Vulgaris
While most warts don’t cause troublesome symptoms, some can cause tightness, itching, or a feeling of pressure. Warts such as those that develop on the feet can be painful. They are usually rough and frequently have a pattern of small, black dots. These black dots are clotted blood vessels. It can take a wart up to 2 to 6 months to grow after exposure to the virus. Common symptoms of viral warts include fleshy, small, and grainy bumps, black pinpoints, and a rough texture. Viral warts are round or oval-shaped, raised and firm, have a rough, irregular surface, and have a 1-to-10 mm diameter.
 You should consult a specialist for your wart if you tried treatment, but the wart persists, spreads, or recurs. You should also consult a specialist if your wart becomes painful or changes in color or appearance. Warts can become more bothersome and interfere with a variety of daily activities. Knowing when you have a foot wart as soon as possible can impact the pain, spread, and treatment options. You should seek a specialist for proper evaluation of your wart if it begins to affect your ability to participate in daily activities, if you have pre-existing diabetes, or if you have a loss of sensation, as these symptoms indicate a worsening condition.
You should consult a specialist for your wart if you tried treatment, but the wart persists, spreads, or recurs. You should also consult a specialist if your wart becomes painful or changes in color or appearance. Warts can become more bothersome and interfere with a variety of daily activities. Knowing when you have a foot wart as soon as possible can impact the pain, spread, and treatment options. You should seek a specialist for proper evaluation of your wart if it begins to affect your ability to participate in daily activities, if you have pre-existing diabetes, or if you have a loss of sensation, as these symptoms indicate a worsening condition.
What Causes Viral Warts?
Immersing your hands in water can contribute to the development of warts as they often spread due to infected close contacts such as in public showers or swimming pools. You can develop HPV warts by going barefoot. Viral warts usually grow on the hands, often on the fingers and palms. While HPV causes warts, there are more than 100 HPV types, and only a few cause hand warts. Most HPV types spread through shared items, such as washcloths or towels, or casual skin contact. You can acquire other HPV strains from sexual contact.
The main types of warts are common, filiform, flat, genital, periungual, plantar, and palmar. Common warts develop on the elbows, fingers, knees, or face. Filiform warts develop on the lips, eyelids, face, or neck. Flat warts appear in clusters on the backs of the hands, face, or legs. Genital warts develop around or on the genitals. Periungual warts appear as thick skin around the nails. Plantar warts grow on the soles of the feet. Palmar warts grow on the palms of the hands. The different HPV types cause different types of HPV warts. The common causes are close contact with a current carrier or a weak immune system.
How Contagious Are Warts?
Warts aren’t highly contagious but can develop from close skin contact with someone who has one or more warts. Warts can also transfer indirectly from surfaces or objects, for example, the area around a swimming pool. You are at a higher risk if your skin is wet or damaged. Some steps you can take to decrease your risk of developing warts are cleaning your feet daily, wearing clean and dry socks, regularly inspecting your feet, carefully cutting your nails, regularly cutting your nails, wearing properly-fitted shoes, moisturizing your feet nightly, and maintaining proper blood sugar levels.
 Treatment for Warts
Treatment for Warts
There is a range of treatment options for your warts depending on the severity of your symptoms and pain. Your specialist will usually begin by examining your wart and scraping off the top layer. They will scrap off this top layer to check for signs of dark dots. They may remove a minor section of the wart and send it to a lab for closer analysis. This lab analysis can help to rule out other skin growth types. A specialist will begin with the most conservative treatment options, including stronger peeling medicine, freezing, and other acids. If these prove ineffective, they may suggest minor surgery or laser treatment.
Effective Treatment of Your Warts
Warts have many causes from different HPV types and develop on various body parts. To avoid significant spreading, pain, and debilitation, see the Foot & Ankle Specialists of Illinois today for effective diagnosis and treatment of your warts.

